Draw and explain the amplitude-frequency graph of an object in resonance.
Important Questions on Sound
The stem of the tuning fork is pressed against a tabletop. Answer the following questions:
(i) Would the above action produce any audible sound?
(ii) Does the above action cause the table to set into vibrations?
(iii) If the answer is yes, what type of vibrations are they?
(iv) Under what conditions do the above action lead to resonance?
A vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of a burette filled with water. The tap is opened and the water level gradually falls. It is observed that the sound becomes the loudest for a particular length of air column.
What is the name of the phenomenon taking place when sound is produced for another length of air column and is not the loudest?
In fig. 7.15,A, B, C and D represent test tubes each of height 20cm which are filled with water up to heights of 12cm, 14cm, 16cm, 18cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of test tube D, a loud sound is heard.
(c) State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
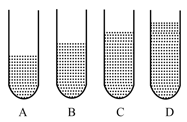
In fig. 7.15,A, B, C and D represent test tubes each of height 20cm which are filled with water up to heights of 12cm, 14cm, 16cm, 18cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of test tube D, a loud sound is heard.
(b) Give the reason for your observation in each case.
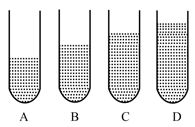
In the figure, A, B, C, and D represent test tubes each of height which is filled with water up to heights of respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of test tube D, a loud sound is heard. Describe the observations with tubes A, B, and C when the vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of these tubes.