Draw ray diagrams to describe the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object when it is placed at

Important Questions on Light : Reflection and Refraction
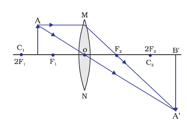
Study the ray diagram given and answer the following questions:
(i) State the type of lens used in the figure.
(ii) List two properties of the image formed.
(iii) In which position of the object will the magnification be
To find the image for varying object distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he moves the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image-does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happens when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A concave lens made of a material of refractive index is kept in medium of refractive index . A parallel beam light is incident on the lens. Complete the path of rays of light emerging from the concave lens if
(a) Two lenses have power of (i) (ii) . What is the nature of focal length of each lens?
(b) An object is kept at a distance of from each of the above lenses. Calculate (i) image distance (ii) magnification in each of two cases.
One half of a convex lens of focal length is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
A tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length . The distance of the object from the lens is . Find the nature, position and size of the image.
