Draw the force-displacement graph for a spring.
Important Questions on Matter and Materials
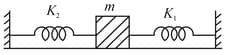
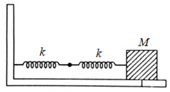
A mass is attached to two springs as shown in figure. The spring constants of two springs are and For the frictionless surface, the time period of oscillation of mass is
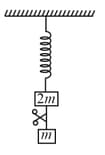
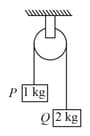
The two blocks and are connected by a metal wire with breaking stress through a frictionless pulley. The minimum radius of the wire for it not to break is (consider )
As shown in the figure, an iron block of volume is attached to a spring of unstretched length and hanging to the ceiling of a roof. The spring gets stretched by . This block is removed and another block of iron of volume is now attached to the same spring and kept on a frictionless incline plane of inclination. The distance of the block from the top along the incline at equilibrium is
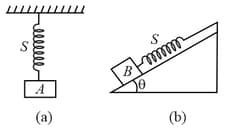
Two identical springs are connected to mass as shown . If the period of the configuration in (i) is , the period of the configuration (ii) is:
I 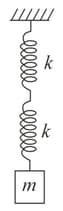
II 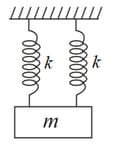
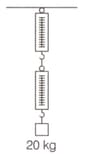
A block of mass is suspended through two spring balances with negligible mass as shown in figure. What will be the readings in the upper and lower balance respectively ?
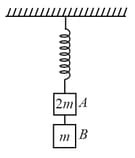
Two blocks, and of masses, and , respectively, are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of and , immediately after the string is cut, respectively are
Reason: Action and reaction force acts in opposite direction.
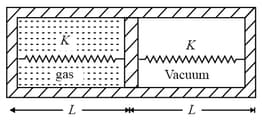
Area of piston is 1 m2. When heat is supplied to the gas it expands and displaces piston by where L = 1m. Natural length of springs is L = 1m. Spring constant K = 100 N/m. The pressure of gas in final situation is –