MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
During an experiment an ideal gas obeys a law Constant. The gas is initially at temperature and volume When gas expands to a volume its temperature will be Value of is
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
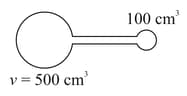
Consider two glass spheres of volume and which are connected by a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown. Initially pressure inside this apparatus is of mercury and its temperature is Now if bulb is kept of and is kept at then new pressure inside the apparatus will be,
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
