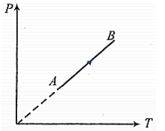
During the process $A B$ of an ideal gas,

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
Using equipartition of energy, the specific heat (in ) of Aluminium at high temperature can be estimated to be (atomic weight of Aluminium )
( is universal gas constant and is the acceleration due to gravity)
Consider an ideal gas confined in an isolated closed chamber. As the gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion, the average time of collision between molecules increases as , where is the volume of the gas. The value of is:
(Atmospheric pressure = of Hg)
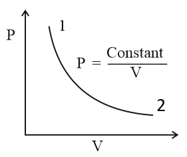
Out of the following which one correctly represents the diagram?
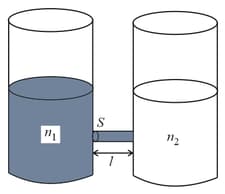
As shown schematically in the figure, two vessels contain water solutions (at temperature ) of potassium permanganate of different concentrations and molecules per unit volume with When they are connected by a tube of small length and cross-sectional area starts to diffuse from the left to the right vessel through the tube. Consider the collection of molecules to behave as dilute ideal gases and the difference in their partial pressure in the two vessels causing the diffusion. The speed of the molecules is limited by the viscous force on each molecule, where is a constant. Neglecting all terms of the order . Which of the following is/are correct? ( is the Boltzmann constant)