Explain homogeneous equilibrium with the help of an example.
Important Questions on Equilibrium
Graph of a reversible process;
is given. Analyse the graph and answer the following question.
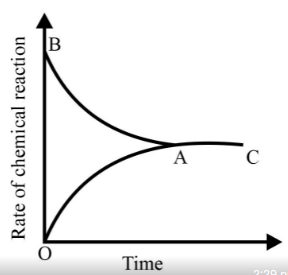
Identify the part of the graph which represents the forward reaction
[ OA, BA, AC]
observed pressure for the reaction mixture in equilibrium is at . What is the value of for the reaction?
Using the data provided, find the value of equilibrium constant for the following reaction at and atm pressure.
(At )
For the reaction
if the initial concentration of and moles of is consumed at equilibrium, the correct expression of is.
For a reaction at equilibrium
the relation between dissociation constant , degree of dissociation and equilibrium pressure is given by :
(assuming ideality)
| Initial Concentration (A) | Initial Concentration (B) | Initial rate of formation of C |
|---|---|---|
The rate law for the formation of is
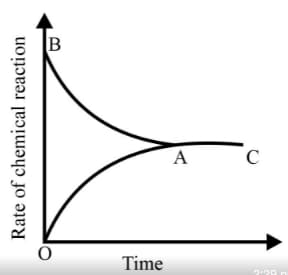
Graph of a reversible process,
is given. Analyse the graph and answer the following question.
From the given statements, select the correct ones regarding chemical equilibrium.
(i0 The chemical equilibrium is 'static' at the molecular level.
(ii) Both reactants and products co-exist.
(iii) The rates of forward reaction and backward reactions are equal.
(iv) Chemical equilibrium is attained in an open system.
At equilibrium, the mass of each of the reactants and products remains constant.
At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.

