Explain paraxial approximation.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Curved Surface
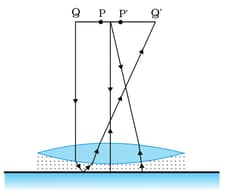
Determine the ‘effective focal length’ of the combination of the two lenses, concave and convex, if they are placed apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of effective focal length of this system useful at all? The focal length of the concave lens and the focal length of the convex lens.
A card sheet divided into squares each of size is being viewed through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length ) held close to the eye. What should be the distance between the object in and the magnifying glass if the virtual image of each square in the figure is to have an area of . Would you be able to see the squares distinctly with your eyes very close to the magnifier?

