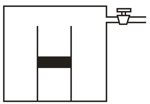
Figure () shows a cylindrical tube of length which is partitioned by a tight-fitting separator. The separator is very weakly conducting and can freely slide along the tube. Ideal gases are filled in the two parts of the vessel. In the beginning, the temperature in parts and are and , respectively. The separator slides to a momentary equilibrium position, shown in the figure. Find the final equilibrium position of the separator, reached after a long time.


Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
A vessel of volume contains an ideal gas at pressure , and temperature . Gas is continuously pumped out of this vessel at a constant volume-rate , keeping the temperature constant. The pressure of the gas being taken out equals the pressure inside the vessel. Find
(a) the pressure of the gas as a function of time.
(b) the time taken before half the original gas is pumped out.
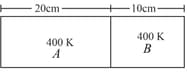
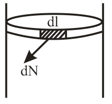
The figure below shows a cylindrical tube of radius and length . It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is . The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of atm and a temperature of . The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches . Let denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length of the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate .
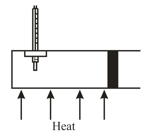
The following figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is , and its pressure is which equals the atmospheric pressure.
(a) What is the tension in the wire?
(b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to ?

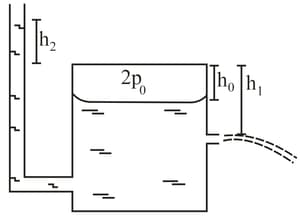
The figure given below shows a large closed cylindrical tank containing water. Initially, the air trapped above the water surface has a height and pressure where is the atmospheric pressure. There is a hole in the wall of the tank at a depth below the top from which the water comes out. A long vertical tube is connected as shown.
(a) Find the height of the water in the long tube above the top initially.
(b) Find the speed with which water comes out of the hole.
(c) Find the height of the water in the long tube above the top when the water stops coming out of the hole.
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of the cross-sectional area of and weight of . The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure . The length of the gas column is . If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.