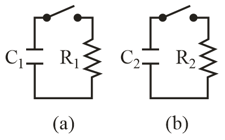
Figure and displays two circuits with a charged capacitor that is to be discharged through a resistor when the switch is closed. In Fig. , , In Fig., and . The ratio of the initial charges on the two capacitors is . At time both switches are closed. At what time do the two capacitors have the same charge?


Important Questions on Circuits
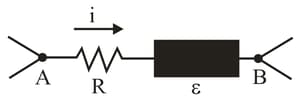
In fig., circuit section absorbs energy at a rate of when current passes through it in the indicated direction. Resistance
What is the potential difference between and Emf device lacks internal resistance.
What is its emf?
Is point connected to the positive terminal of or to the negative terminal?
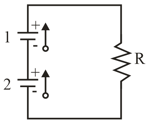
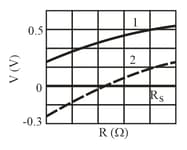
In fig., both batteries have emf and the external resistance is a variable resistor. Fig., , gives the electric potential between the terminals of each battery as functions of Curve corresponds to battery and curve corresponds to battery . The horizontal scale is set by What is the internal resistance of battery and battery
(a) (b)
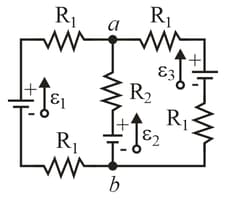
In figure, the resistances are and and the ideal batteries have emfs and What are the size, direction (up or down) of the current in battery and the size, direction of the current in battery Is battery absorbing or providing energy and at what rate? What is the potential difference
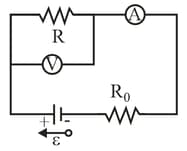
In the following figure, a voltmeter of resistance and an ammeter of resistance are being used to measure a resistance in a circuit that also contains a resistance and an ideal battery of emf . Resistance is given by , where is the voltmeter reading and is the current in resistance . However, the ammeter reading is not but rather which is plus the current through the voltmeter. Thus, the ratio of the two meter readings is not but only an apparent resistance . If , what are (a) the ammeter reading, (b) the voltmeter reading, and (c) ? (d) If is increased, does the difference between and increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A resistor and a capacitor are connected in series with an ideal battery of emf . At after the connection is made, what is the rate at which
(a) the charge of the capacitor is increasing?
(b) energy is being stored in the capacitor?
(c) thermal energy is appearing in the resistor?
(d) energy is being delivered by the battery?
