EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Figure gives the acceleration of a body as it moves from rest along axis while a variable force acts on it from to . The work done by the force on the body when it reaches
(i) and
(ii) shall be as given below.
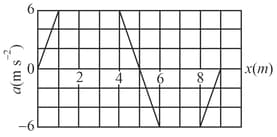
(i) and
(ii) shall be as given below.

(a) and respectively
(b) and respectively
(c) and respectively
(d) and respectively
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
HARD
NEET
IMPORTANT
A force acts on a particle in such a way that the position of the particle as a function of time is given by where is meters and is in seconds. The work done during the first second is
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A constant force is applied to a body of mass moving with initial velocity . If after the body undergoes a displacement , its velocity becomes , then the total work done is,
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
The graph between kinetic energy and velocity is
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Velocity-time graph of a particle of mays moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. Work done by all the forces on the particle is
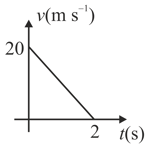
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
The kinetic energy of a body becomes four times its initial value. The new momentum will be.
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A ball is thrown up with an initial speed and reaches a maximum height of How much energy is dissipated by the air drag acting on the ball during ascent?
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A ball of mass and another of mass are dropped together from a feet tall building. After a fall of feet each towards earth, their respective kinetic energies will be in the ratio of
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Two bodies of mass and have equal then ratio of their momentum is
