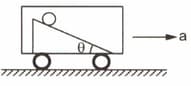
Figure shows a smooth inclined plane fixed in a car accelerating on a horizontal road. The angle of incline is related to the acceleration of the car as . If the sphere is set in pure rolling on the incline,


Important Questions on Rigid Body Dynamics: Part 2
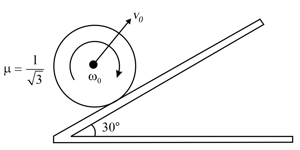
A sphere is moving on a smooth surface with linear speed and angular velocity It finds a rough inclined surface and it starts climbing up:
A sphere, a ring and a disc of same mass and radius are allowed to roll down three similar sufficiently rough inclined planes as shown in the figure from same height.
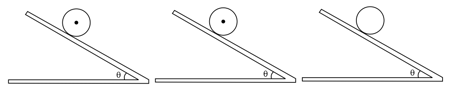
Which of the following order is true for final of the bodies?
A sphere rolling on a horizontal rough surface collides elastically with a smooth vertical wall, as shown in figure. State which of the following statements is true or false <
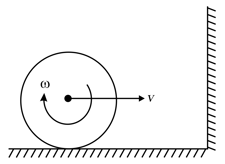
(a) After collision, the velocity of the centre of mass gets reversed.
(b) Angular momentum of the sphere about the point of contact with the wall is conserved.
(c) Angular momentum of the sphere about a stationary point on the horizontal surface is conserved.
(d) Just after collision the point of contact with the horizontal surface is moving towards the wall.
(e) After collision the friction force acts on the sphere such that it decreases the linear speed and increases the angular speed.
(f) Finally, when the sphere starts rolling, it is moving away from the wall.
A uniform bar of length and mass lies on a smooth horizontal table. Two point masses and moving in opposite direction in the same horizontal plane with speed and respectively, strike the bar and stick to the bar after collision. Calculate
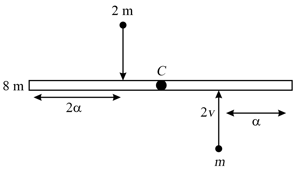
(a) the velocity of the centre of mass after collision
(b) the angular velocity of the centre of mass after collision
(c) total energy
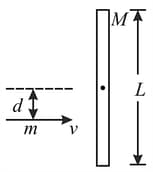
A rod of mass and length lies on a smooth horizontal surface. A particle, of mass and velocity strikes the rod perpendicular to its length, as shown in figure. As a result of the collision, the centre of mass of the rod attains a speed of and the particle rebounds back with a speed of Find the following:
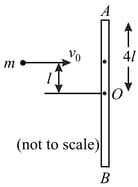
(a) The ratio
(b) The angular velocity of the rod about
(c) The coefficient of restitution for the collision.
(d) The velocities of the ends and of the rod, namely, and respectively.
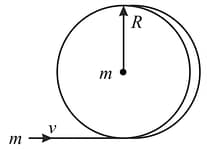
A circular wooden hoop of mass and radius rests flat on a frictionless surface. A bullet, also of mass and moving with a velocity , strikes the
hoop and gets embedded in it. The thickness of the hoop is much smaller than . Find the angular velocity with which the system rotates after the bullet strikes the hoop.
A stick of length and mass lies on a frictionless horizontal surface on which
it is free to move in anyway. A ball of mass moving with speed collides
elastically with the stick. What must be the mass of the ball so that it remains at
rest immediately after collision?