Find the pressure of air in a vessel being evacuated as a function of evacuation time . The vessel's volume is and initial pressure is The process is assumed to be isothermal and the evacuation rate equal to , and independent of pressure.
Note: The evacuation rate is the gas volume being evacuated per unit time, with that volume being measured under the gas pressure attained by that moment.

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
Find the maximum attainable temperature of an ideal gas, in each of the following processes,
(a) ,
(b) ,
where, and are the positive constants and is the volume of one mole of gas.
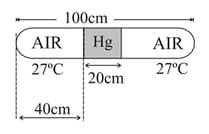
In the given figure a glass tube lies horizontally with the middle containing mercury. The two ends of the tube contains air at and at a pressure of mercury. Now the air column on one side is maintained at and the other side is maintained at . Find the new length of the air column on the cooler side. Neglect the changes in the volume of mercury and of the glass.