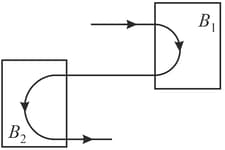
Following figure shows the path of an electron that passes through two regions, containing uniform magnetic fields of magnitudes and . Its path in each region is a half circle. Choose the correct option.


Important Questions on Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces
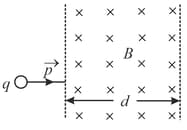
A particle with charge , moving with a momentum enters a uniform magnetic field normally. The magnetic field has magnitude and is confined to a region of width , where The particle is deflected by an angle in crossing the field
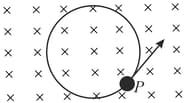
A particle having a charge of and mass moves in a circle of radius under the influence of a magnetic field of induction . When the particle is at a point , a uniform electric field is switched on so that the particle starts moving along the tangent with a uniform velocity. The electric field is
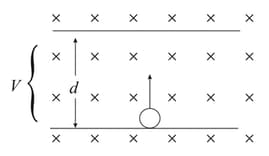
In the below figure, an electron of mass , charge , and low (negligible) speed, enters the region between two plates of potential difference and plate separation , initially headed directly towards the top plate. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude is normal to the plane of the figure. Find the minimum value of , such that the electron will not strike the top plate.
Bainbridge’s mass spectrometer separates ions having the same velocity. The ions, after entering through slits, , pass through a velocity selector composed of an electric field produced by the charged plates and and a magnetic field perpendicular to the electric field and the ion path. Ions that then pass undeviated through the crossed field enter into a region where a second magnetic field exists, where they are made to follow circular paths. A photographic plate (or a modern detector) registers their arrival. If is the radius of the circular orbit, then specific charge of ion is
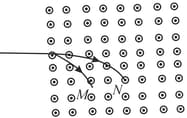
Two charged particles and enter a space of uniform magnetic field with velocities perpendicular to the magnetic field. The paths are as shown in the figure. The possible reason for different paths may be