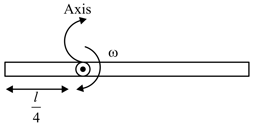
For a rigid circular body rotating about its axis with a constant angular speed, the magnitude of the velocity of particles situated at one of its radii:
Important Questions on Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body
Figure below shows a shampoo bottle in a perfect cylindrical shape
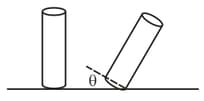
In a simple experiment, the stability of the bottle filled with different amount of shampoo volume is observed. The bottle is tilted from one side and then released. Let the angle depicts the critical angular displacement resulting in the bottle losing its stability and tipping over. Choose the graph correctly depicting the fraction of shampoo filled ( corresponds to completely filled) vs the tipping angle .
A plank is moving in a horizontal direction with a constant acceleration . A uniform rough cubical block of side rests on the plank and is at rest relative to the plank.
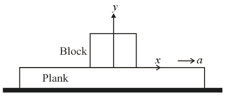
Let the centre of mass of the block be at at a given instant. If , then the normal reaction exerted by the plank on the block at that instant acts at
A wide bottom cylindrical massless plastic container of height has identical coins inside it and is floating on water with inside the water. If we start putting more of such coins on its lid, it is observed that after coins are put, its equilibrium changes from stable to unstable. Equilibrium in floating is stable if the geometric center of the submerged portion is above the center of mass of the object). The value of is closest to
(i) Centre of mass of a body always coincides with the centre of gravity of the body.
(ii) Centre of mass of a body is the point at which the total gravitational torque on the body is zero
(iii) A couple on a body produce both translational and rotational motion in a body.
(iv) Mechanical advantage greater than one means that small effort can be used to lift a large load.
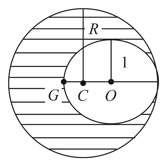
As shown in figure, when a spherical cavity (centred at ) of radius is cut out of a uniform sphere of radius (centred at ), the centre of mass of remaining (shaded part of sphere is at i.e., on the surface of the cavity. can be determined by the equation:
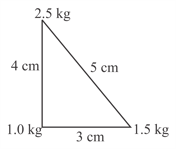
Three point particles of masses and are placed at three corners of a right angle triangle of sides and as shown in the figure. The centre of mass of the system is at a point:
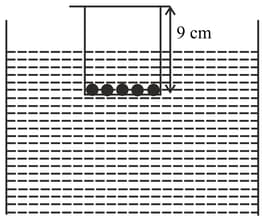
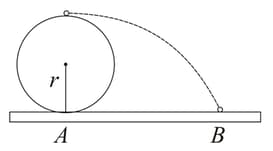
A wheel of radius "rolls without slipping with a speed on a horizontal road. When it is at a point on the road a small bob of the mud separates from wheel at the highest point and touches the point on the road as shown in the figure. Then is (g-acceleration due to gravity)
A rigid massless rod of length has two masses attached at each end as shown in the figure. The rod is pivoted at point on the horizontal axis. When released from the initial horizontal position, its instantaneous angular acceleration will be
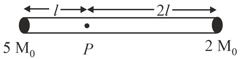
A uniform rod of mass and length is suspended by two vertical inextensible strings as shown in figure. Calculate tension in left string at the instant, when right string snaps.
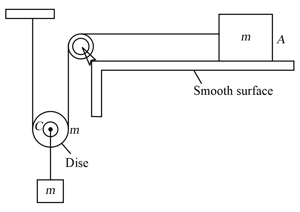
In the figure and are identical blocks, each of mass and is a circular disc of equal mass . Pulley is massless and ffictionless and thread is inextensible. Neglecting friction, find the acceleration of block and .
A uniform rod rotates in a vertical plane about the shown axis. Angular velocity at the moment is . Then, force on the rod by the axis at the moment