HOW IS lens magnification calculated?
Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surface and Spherical Lens
For which position of the object, magnification of convex lens is -1 (minus one)?
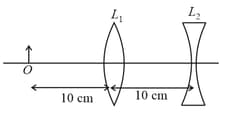
An extended object is placed at point , in front of a convex lens and a concave lens is placed behind it, as shown in the figure. The radii of curvature of all the curved surfaces in both the lenses are . The refractive index of both the lenses is . The total magnification of this lens system is:
Use the lens equation and prove that for a convex lens when the object is placed within the focal length, the image will be virtual.
A point object is placed on the axis of a thin convex lens of focal length at a distance of from the lens and its image is formed on the axis. If the object is now made to oscillate along the axis with a small amplitude of , then what is the amplitude of oscillation of the image?
[you may assume, where
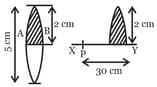
A focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20 cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25cm in front of it to 50cm, the magnification of its image changes from The ration is

