MEDIUM
Earn 100
How to calculate number of moles of solute from ebullioscopic constant?
Important Questions on Chemical kinetics
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
product
| Experiment | Initial rate of reaction | ||
The time (in minutes) required to consume half of is
HARD
Consider the given plots for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation (and are rate constant and activation energy, respectively )
(I)
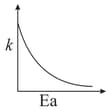
(II)
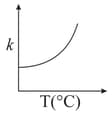
MEDIUM
| [A] | [B] | [C] | Rate |
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
For a reaction, consider the plot of versus given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at is , then the rate constant at is:
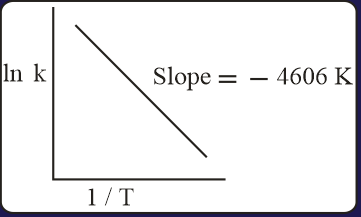
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
Which one of the following statements is correct?
MEDIUM
HARD
For an elementary chemical reaction, , the expression for is:
EASY
EASY
HARD
The activation energy of the backward reaction exceeds that of the forward reaction by (in ). If the pre-exponential factor of the forward reaction is times that of the reverse reaction, the absolute value of for the reaction at is ____.
(Given; and is the Gibbs energy)
HARD
(Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases)
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY

