is a crystalline solid. It is a molecular solid in which molecules are held together with van der Waals forces. Given diagram represents two adjacent molecules in solid.
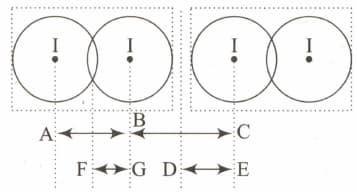
If length and covalent radius of iodine is
Find the Van der Waals radius of atom.


Important Questions on Periodic Classification of Elements and General Inorganic Chemistry
is a crystalline solid. It is a molecular solid in which molecules are held together with van der Waals forces. Given diagram represents two adjacent molecules in solid.
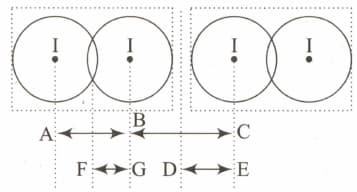
If length and covalent radius of iodine is
Which of the following data is smaller as compared toAccording to Slater effective nuclear charge, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge of the nucleus of the atom. depends on the type of orbital In which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons
in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is The effective nuclear charge due to screening is given by where is the atomic number and is the slater screening constant values:
| Electrons in orbitals |
per electron in orbital | ||
| etc. | |||
| or orbital | |||
| or orbital | |||
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbital, is not considered in calculation of
What is the value of for
According to Slater effective nuclear charge, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge of the nucleus of the atom. depends on the type of orbital In which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons
in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is The effective nuclear charge due to screening is given by where is the atomic number and is the slater screening constant values:
| Electrons in orbitals |
per electron in orbital | ||
| etc. | |||
| or orbital | |||
| or orbital | |||
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbital, is not considered in calculation of
What is for
According to Slater effective nuclear charge, due to screening, is not exactly equal to the actual nuclear charge of the nucleus of the atom. depends on the type of orbital In which the electron is housed, and on the ability of other electrons
in more penetrating orbitals to screen the electron in question from the nucleus.
The relative extent to which the various orbitals penetrate the electron clouds of other orbitals is The effective nuclear charge due to screening is given by where is the atomic number and is the slater screening constant values:
| Electrons in orbitals |
per electron in orbital | ||
| etc. | |||
| or orbital | |||
| or orbital | |||
Screening effect of one electron in the outermost orbital, is not considered in calculation of
In which of the following cases the concept of is applicable?
The first and the second ionisation enthalpies of a few elements designated by Roman numerals are shown below:
| Element | ||
| I | ||
| II | ||
| III | ||
| IV |
Which of the above elements is likely to be:
A reactive metal:
The first and the second ionisation enthalpies of a few elements designated by Roman numerals are shown below:
| Element | ||
| I | ||
| II | ||
| III | ||
| IV |
Which of the above elements is likely to be:
A reactive non-metal:
The first and the second ionisation enthalpies of a few elements designated by Roman numerals are shown below:
| Element | ||
| I | ||
| II | ||
| III | ||
| IV |
Which of the above elements is likely to be:
A noble gas.
