If (where P denotes pressure in atm and d denotes density in ) is plotted for gas (ideal gas) at a particular temperature. If , then the temperature will be:

Important Questions on States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
A vessel of uniform cross-section of length as shown figure is divided in two parts by a weightless & frictionless piston one part contains moles of and other part contains moles of mole of gaseous mixture at the same temperature and pressure.
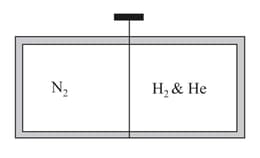
What is the length of compartment?
(Assume volume of piston to be negligible)
In two different vessels and containing at the same temperature, the vacant space left over the surface of is and . What is the ratio of of vapour's in two vessels?
What is the mass of present in air in litre closed vessel with relative humidity at and ?
Given: Vapour pressure of is torr at .
Berthelot proposed the following empirical relation to explain the real behaviour of the real gases :
If the Berthelot equation of state be one of the forms of virial equation for 1 mole real gas is as under:
where A, B and C are constants which are known as second, third and fourth virial coefficients respectively. Then what will be the correct value of Boyle's temperature i.e., i.e., the temperature at which i.e., ideal gas equation is obeyed?
