MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
If angular velocity of a disc depends an angle rotated as , then its angular acceleration at rad is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)None of these
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Circular Motion
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
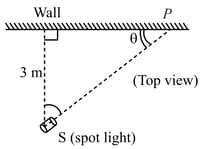
A spot light rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of . The spot of light moves along the wall at a distance . What is the velocity of the spot when ?
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
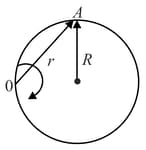
A particle moves along a circle of radius so that its radius vector relative to the point (figure) rotates with the constant angular velocity . Then modulus of the velocity of the particle, and the modulus of its total acceleration will be