EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
If the mean free path of gaseous molecules is at a pressure of , what will be its mean free-path when the pressure is increased by 100 times ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
75% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
The mean free path for a gas, with molecular diameter and number density can be expressed as:
MEDIUM
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas in a closed container is slowly heated. As its temperature increases, which of the following statements are true ?
(A) the mean free path of the molecules decreases
(B) the mean collision time between the molecules decreases.
(C) the mean free path remains unchanged.
(D) the mean collision time remains unchanged.
MEDIUM
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
The plot that depicts the behavior of the mean free time (time between two successive collisions) for the molecules of an ideal gas, as a function of temperature qualitatively, is: (Graphs are schematic and not drawn to scale)
MEDIUM
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas is enclosed in a cylinder at pressure of atm and temperature, The mean time between two successive collisions is If the pressure is doubled and temperature is increased to the mean time between two successive collisions will be close to:
MEDIUM
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A certain sample of a gas has a volume of measured at pressure and . At the same pressure but , its volume will be
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A constant volume gas thermometer shows pressure reading of and of mercury at and respectively. When the pressure reading is of mercury, the temperature is
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
For the diagram given for an ideal gas
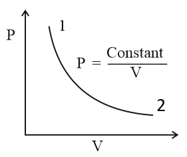
Out of the following which one correctly represents the diagram?
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
By what percentage should the pressure of the given mass of gas be increased so to decrease its volume by 10% at a constant temperature?
