EASY
Earn 100
In Fraunhofer diffraction experiment, L is the distance between screen and the obstacle, b is the size of obstacle and . is wavelength of incident light. The general condition for the applicability of Fraunhofer diffraction is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Optics
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
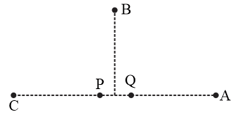
In the figure below, and are two equally intense coherent sources emitting radiation of wavelength The separation between and is and the phase of is ahead of that of by and C are three distinct point of observation, each equidistant from the midpoint of PQ. The intensities of radiation at will be in the ratio :
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
EASY
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY

