In a YDSE a parallel beam of light of wavelength is incident on slits at angle of incidence . and are two thin transparent films each of refractive index . Thickness of is . Light coming through and have intensities and respectively on the screen. Intensity at point which is symmetric relative to the slits is . The central maxima is above .
(i) What is the maximum thickness of to do so. Assuming thickness of to be that found in part (i) answer the following parts.
(ii) Find fringe width, maximum intensity and minimum intensity on screen.
(iii) Distance of the nearest minima from .
(iv) Intensity at on either side of .
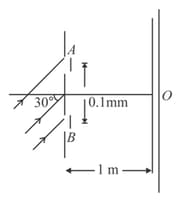
(i) What is the maximum thickness of to do so. Assuming thickness of to be that found in part (i) answer the following parts.


Important Questions on Wave Optics
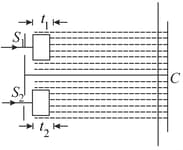
A screen is at a distance from a diaphragm having two narrow slits and which are apart. Slit is covered by a transparent sheet of thickness and by another sheet of thickness as shown in figure. Both sheets are made of same material having refractive index .
Water is filled in space between the diaphragm and screen. A monochromatic light beam of wavelength is incident normally on the diaphragm. Assuming intensity of beam to be uniform and slits of equal width, calculate ratio of intensity at C to maximum intensity of interference pattern obtained on the screen, where is foot of perpendicular bisector of . (Refractive index of water, )
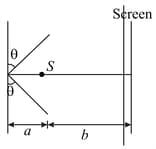
Two plane mirrors, a source of light, emitting monochromatic rays of wavelength and a screen are arranged as shown in figure. If angle is very small, calculate fringe width of the interference pattern formed by reflected rays.
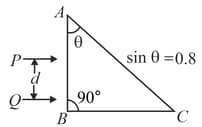
Two parallel beams of light and (separation ) containing radiations of wavelengths and (which are mutually coherent in each wavelength separately) are incident normally on a prism as shown in figure The refractive index of the prism as a function of wavelength is given by the relation, , where is in and is a positive constant.
The value of is such that the condition for total reflection at the face is just satisfied for one wavelength and is not satisfied for the other. A convergent lens is used to bring these transmitted beams into focus. If the intensities of the upper and the lower beams immediately after transmission from the face , are and respectively, find the resultant intensity at the focus.
A narrow monochromatic beam of light of intensity is incident on a glass plate as shown in figure. Another identical glass plate is kept close to the first one & parallel to it. Each glass plate reflects of the light incident on it & transmits the remaining. Find the ratio of the minimum & the maximum intensities in the interference pattern formed by the two beams obtained after one reflection at each plate.
A monochromatic light of frequency is incident on two identical metal spheres of threshold frequency and respectively. After some time, emission of photoelectron will stop on both spheres. Now both metal spheres are connected through wire. (Radius of spheres is )
(i) What will be potential of spheres now?
(ii) How many electron will flow through wire?
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength f falls on a photocell operating in saturating mode. The corresponding spectral sensitivity of photocell is . When another monochromatic radiation of wavelength and power is incident, it is found that maximum velocity of photoelectrons increases times. Assuming efficiency of photoelectron generation per incident photon to be same for both the cases, calculate
(i) threshold wavelength for the cell.
(ii) saturation current in second case.
