In a cylinder, moles of an ideal monatomic gas initially at and expands until its volume doubles. Compute the work done if the expansion is adiabatic?

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
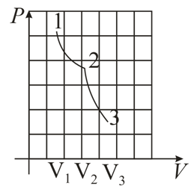
One mole of a perfect gas, initially at a pressure and temperature of and , respectively, expands isothermally until its volume is doubled and then adiabatically until its volume is again doubled. Find the final pressure and temperature of the gas. Find the total work done during the isothermal and adiabatic processes. Given . Also draw the diagram for the process.
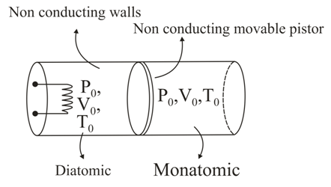
A cylindrical container having nonconducting walls is partitioned in two equal parts such that the volume of the each parts is equal to . A movable nonconducting piston is kept between the two parts. Gas on left is slowly heated so that the gas on right is compressed upto volume . Find pressure and temperature on both sides if initial pressure and temperature, were and respectively. Also find heat given by the heater to the gas. (number of moles in each part is )
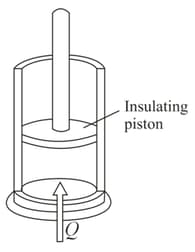
An adiabatic vertical cylinder fitted with and adiabatic frictionless piston contains moles of an ideal diatomic gas. The initial volume and temperature of the gas are and , respectively, with the piston fixed tightly. The atmospheric pressure is . If the piston be released, find the equilibrium temperature and volume of the gas, if the heat capacity of the cylinder and piston is negligibly small. Weight of the piston and cross-sectional area of the cylinder are and . respectively.