In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was reduced by hydrogen gas. The hydrogen was passed over the oxide of copper in a boiling tube with a hole near its end. The excess hydrogen was burnt off at this hole. The copper oxide was placed inside the boiling tube, which was clamped in a horizontal position, in a porcelain boat and heated strongly.
A labelled diagram of the apparatus is
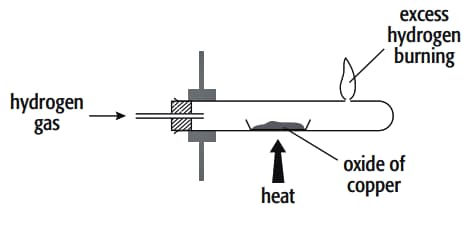

Important Questions on Practical Skills-2
Diffusion in a gas is the random motion of particles involved in the net movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The process of diffusion also takes place in solution. Medical scientists are interested in the rate of diffusion of pharmaceutical compounds through tumours. They can model the factors that affect the rate of diffusion of these drugs by conducting investigations using coloured compounds (to model the drugs) and gelatin, a jelly-like substance (to model the tumours).
The kinetic energy of particles depends on their mass and the speed they travel at. So at a given temperature, large particles will travel slower on average than smaller particles.
Imagine that you are a member of a research team trying to find out how the rate of diffusion through gelatin depends on the relative molecular mass of a drug.
_____ of diffusion is an independent variable.
In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was reduced by hydrogen gas. The hydrogen was passed over the oxide of copper in a boiling tube with a hole near its end. The excess hydrogen was burnt off at this hole. The copper oxide was placed inside the boiling tube, which was clamped in a horizontal position, in a porcelain boat and heated strongly.
The products formed in this reaction are
A learner weighed a mass of of the oxide of copper oxide on a balance reading to the nearest . What was the percentage error in this measurement?
A student noticed that the leaves on a plant growing close to a wall had two sorts of leaves. The leaves next to the wall were in the shade and looked different from the leaves on the side away from the wall that were exposed to the sun. The length of the internodes on the stem also looked different.
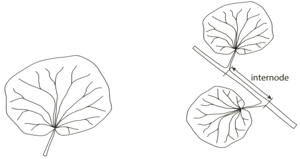
The figure on the left shows the leaf shape. The figure on the right shows an internode. The student decided to investigate the differences by measuring some features of 30 leaves and internodes from each side of the plant.
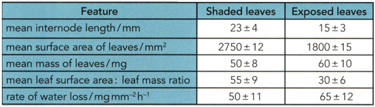
Based on this answer the following question.
The types of leaves is _____ variable.In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was reduced by hydrogen gas. The hydrogen was passed over the oxide of copper in a boiling tube with a hole near its end. The excess hydrogen was burnt off at this hole. The copper oxide was placed inside the boiling tube, which was clamped in a horizontal position, in a porcelain boat and heated strongly.
The mass of oxygen can be measured by subtracting the mass of (tube and) porcelain boat from the mass of (tube) boat and its contents left after heating.
In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was reduced by hydrogen gas. The hydrogen was passed over the oxide of copper in a boiling tube with a hole near its end. The excess hydrogen was burnt off at this hole. The copper oxide was placed inside the boiling tube, which was clamped in a horizontal position, in a porcelain boat and heated strongly.
The mass of oxygen can be measured by subtracting the mass of (tube) boat and its contents left after heating from the mass of (tube) boat and oxide of copper before heating.
Diffusion in a gas is the random motion of particles involved in the net movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The process of diffusion also takes place in solution. Medical scientists are interested in the rate of diffusion of pharmaceutical compounds through tumours. They can model the factors that affect the rate of diffusion of these drugs by conducting investigations using coloured compounds (to model the drugs) and gelatin, a jelly-like substance (to model the tumours).
The kinetic energy of particles depends on their mass and the speed they travel at. So at a given temperature, large particles will travel slower on average than smaller particles.
Imagine that you are a member of a research team trying to find out how the rate of diffusion through gelatin depends on the relative molecular mass of a drug.
Rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane.
In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was reduced by hydrogen gas. The hydrogen was passed over the oxide of copper in a boiling tube with a hole near its end. The excess hydrogen was burnt off at this hole. The copper oxide was placed inside the boiling tube, which was clamped in a horizontal position, in a porcelain boat and heated strongly.
In an experiment to determine the formula of an oxide of copper, the copper oxide was oxidised by hydrogen gas.

