In following circuit potential at point is zero then determine
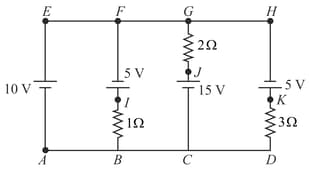
(a) Potential at each point.
(b) Potential difference across each resistance.
(c) Identify the batteries which act as a source.
(d) Current in each battery.
(e) Which resistance consumes maximum power?
(f) Which battery consume or gives maximum power?


Important Questions on Current Electricity
For the circuit shown in figure, find the voltage across resistor and the current passing through it.

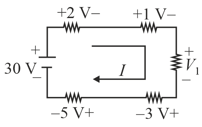
For the circuit shown in the figure, determine the unknown voltage drop .
A resistor develops of thermal energy in when a current of is passed through it. (a) Find its resistance. (b) If the current is increased to , what will be the energy developed in .
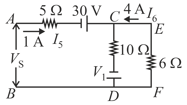
Find the current in resistance, , and source voltage in the circuit shown in figure.
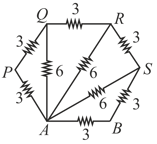
All resistance in diagram (figure) are in ohms. Find the effective resistance between the points
In the given circuit determine
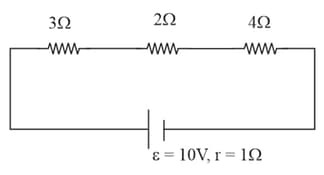
Equivalent resistance (Including internal resistance).
Current in each resistance
Potential difference across each resistance
The rate at which the chemical energy of the cell is consumed
The rate at which heat is generated inside the battery
Electric power output
Potential difference across battery
Resistor that consumes maximum power out of three```````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````
Power dissipated in Resistance.
