In gravity free space, a bead of charge and mass is threaded on a rough rod of friction coefficient A magnetic field of magnitude exists perpendicular to the rod. The bead is projected along the rod with a speed of . How much distance (in ) will the bead cover before coming to rest?

Important Questions on Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
A line charge is fixed on the rim of a wheel of radius which is then suspended horizontally, so that it is free to rotate (the spokes are made of wood). In the central region upto radius , there is uniform magnetic field, pointing up. Now suddenly the field is turned off. If the moment of inertia is , the final angular velocity of the wheel is . Find .
The long, horizontal pair of rails shown in the figure is connected using resistance The distance between the rails is the electrical resistance of the rails is negligible. A conducting wire of mass and length can slide without friction on the pair of rails, in a vertical, homogeneous magnetic field of induction A force of magnitude is exerted for sufficiently long time onto the conducting wire, so that the speed of the wire becomes nearly constant. The force is now removed at a certain point The distance the conducting wire cover on rails from point before stopping is meters. Find (Given : )

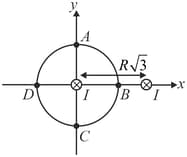
Two current carrying wire of infinite length are placed perpendicular to - plane at and as shown in figure. Current in both the wires is same and inwards to the - plane. Find ratio of in segment to segment will be :
A constant current source as shown in figure is connected across a galvanometer. If galvanometer is shunted by resistance then current in it is reduced to of initial value. If it is further shunted by resistance, current is further reduced by while original current being same. Find value of .