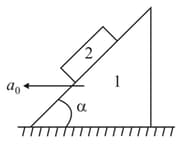
In the arrangement shown in figure the masses of the wedge and the body are known. The appreciable friction exists only between the wedge and the body , the friction coefficient being equal to . The masses of the pulley and the thread are negligible. Find the acceleration of the body relative to the horizontal surface on which the wedge slides.


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
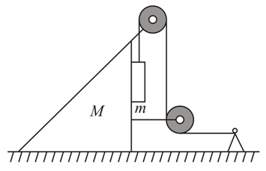
What is the minimum acceleration with which bar (figure) should be shifted horizontally to keep bodies and stationary relative to the bar? The masses of the bodies are equal and the coefficient of friction between the bar and the bodies is equal to . The masses of the pulley and the threads are negligible, the friction in the pulley is absent.
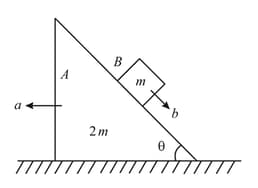
Prism with bar of mass placed on it gets a horizontal acceleration directed to the left (figure). At what maximum value of this acceleration will the bar be still stationary relative to the prism, if the coefficient of friction between them ?
A small spherical ball undergoes an elastic collision with a rough horizontal surface. Before the collision, it is moving at an angle to the horizontal (see figure). You may assume that the frictional force obeys the law during the contact period, where is the normal reaction on the ball and is the coefficient of friction.
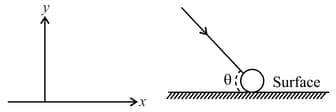
Obtain , so that the subsequent horizontal range of the ball after leaving the horizontal surface is maximised.
Find the allowed range for
A lift is going up. The total mass of the lift and the passengers is . The variation in the speed of the lift is given in the graph.
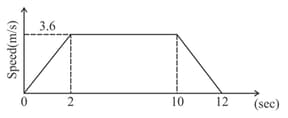
(a) What will be the tension in the rope pulling the lift at equal to
(i) (ii) and (iii) ?
(b) What is the height through which the lift takes the passengers?
(c) What will be the average velocity and average acceleration during the course of entire motion?
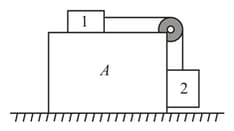
The system shown in figure is released from rest. Calculate the value of accelerations and (where is with respect to )