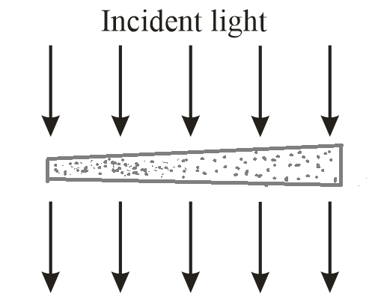
In the below figure, a broad beam of light of wavelength is incident at on a thin, wedge-shaped film with an index of refraction . The transmission gives bright and dark fringes along the film's length. What is the left-to-right change in the film thickness?


Important Questions on Interference
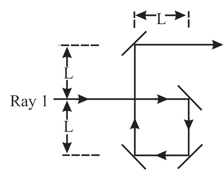
In the below figure, two light rays go through different paths by reflecting from the various flat surfaces shown. The light waves have a wavelength of and are initially in phase. What is the smallest and the second smallest value of distance that will put the waves exactly out of phase as they emerge from the region?
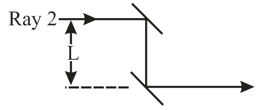
In the following figure, assume that the two light waves, of wavelength in the air, are initially out of phase by . The indexes of refraction of the media are and . What is the smallest and second smallest value of that will put the waves exactly in phase, once they pass through the two media?
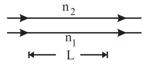
In a double-slit experiment, the fourth-order maximum for a wavelength of occurs at an angle of .
(a) What range of wavelengths in the visible range to is not present in the third-order maxima?
(b) To eliminate all the visible light in the fourth-order maximum, should the slit separation be increased or decreased and (c) What least change is needed?
Three electromagnetic waves travel through a certain point along an -axis. They are polarized, parallel to a -axis, with the following variations in their amplitudes. Find their resultant at .
In the following figure, two light pulses are sent through layers of plastic with thicknesses of either or , as shown, and indexes of refraction and .
Which pulse travels through the plastic in less time?
What multiple of gives the difference in the traversal times of the pulses?

