In the circuit shown all five resistors have the same value and each cell has an emf . Find the open circuit voltage and the short circuit current for the terminals and .


Important Questions on Current Electricity
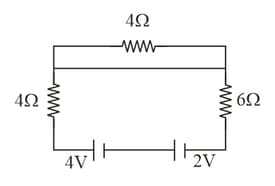
Find the currents through the three resistors shown in figure
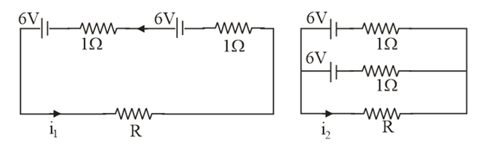
Find the value of in figure if (a) , (b) (c) . Note from your answer that in order to get more current from a combination of two batteries they should be joined in parallel if the external resistance is small and in series if the external resistance is large as compared to the internal resistances.
(a) into an ammeter with a range of .
(b) into a voltmeter with a range of .
A voltmeter of resistance is used to measure the potential difference across the resistor in the circuit shown in the figure.
(a) What will be the reading of the voltmeter?
(b) What was the potential difference across before the voltmeter was connected?
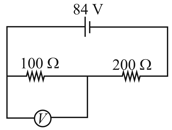
An electrical circuit is shown in the figure. Calculate the potential difference across the resistance of as will be measured by the voltmeter of resistance either by applying Kirchhoff's rules or otherwise.
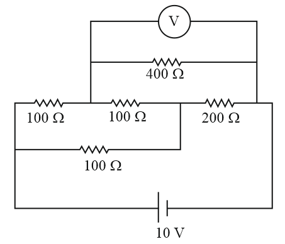
A battery of and internal resistance is connected to a resistor of through an ammeter. The resistance of the ammeter is A voltmeter has also been connected to find the potential difference across the resistor.
Draw the circuit diagram.
The ammeter reads What is the resistance of the voltmeter ?
The voltmeter reads what is the zero error in the voltmeter ?
(Hint : zero error observed reading – actual reading)
In the figure the potentiometer wire of length & resistance is joined to the cell of & internal resistance . The cell s e.m.f. is and its internal resistance is The galvanometer will show no deflection then find length
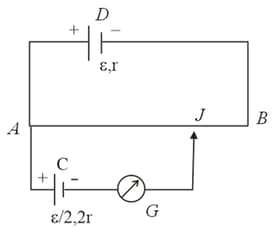
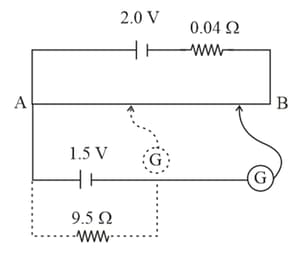
Figure shows a potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of The balance point of the cell without in the external circuit is When a resistor of is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the secondary cell.