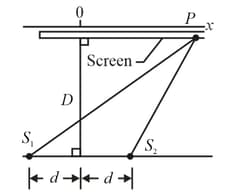
In the figure, two isotropic point sources and emit light in phase at wavelength and at the same amplitude. The sources are separated by distance, . They lie on an axis which is parallel to the -axis which runs along a viewing screen at distance . The origin lies on the perpendicular bisector between the sources. The figure shows two rays reaching point on the screen at position . (a) At what value of do the rays have the minimum possible phase difference? (b) What multiple of gives the minimum phase difference? (c) At what value of do the rays have the maximum possible phase difference? What multiple of gives (d) that maximum phase difference and (e) the phase difference when ? (f) When , is the resulting intensity at point a maximum, a minimum, an intermediate but closer to maximum, or an intermediate but closer to minimum?


Important Questions on Interference
If mirror in a Michelson interferometer is moved through , a shift of bright fringes occurs. What is the wavelength of the light producing the fringe pattern?

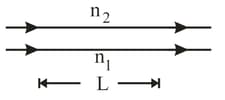
Suppose that two waves have wavelength, in air. What multiple of gives their phase difference when they emerge if (a) and (b) and and (c) and ?
(d) Suppose that in each of these three situations, the waves arrive at a common point (with the same amplitude) after emerging. Rank the situations according to the brightness the waves produce at the common point.
Monochromatic green light of wavelength illuminates two parallel narrow slits which are apart. Calculate the angular deviation of the third-order bright fringe (a) in radians and (b) in degrees.
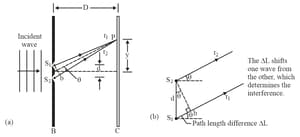
(a) What is the angular separation in radians between the central maximum and an adjacent maximum?
(b) What is the distance between these maxima on a screen from the slits?
