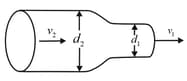
In the figure, water flows through a horizontal pipe and then out into the atmosphere at a speed . The diameter of the left and right sections of the pipe are and . (a) What volume of water flows into the atmosphere during a period? In the left section of the pipe, what are (b) the speed and (c) the gauge pressure ?


Important Questions on Fluids
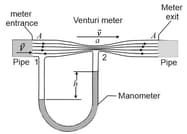
A venturi meter is used to measure the flow speed of a fluid in a pipe. The meter is connected between two sections of the pipe; the cross-sectional area A of the entrance and exit of the meter matches the pipe's cross-sectional area. Between the entrance and exit, the fluid flows from the pipe with speed V and then through a narrow "throat" of cross sectional area a with speed v. A manometer connected the wider portion of the meter to the narrower portion. The change in the fluid's speed is accompanied by a change. in the fluid's pressure, which causes a height difference of the liquid in the two arms of the manometer. (Here means pressure in the throat minus pressure in the pipe,) (a) By applying Bernoulli's equation and the equation of continuity to points and in the figure, show that,
,
where is the density of the fluid. (b) Suppose that the fluid is fresh water, that the cross-sectional areas are in the pipe and in the throat, and that the pressure is in the pipe and in the throat. What is the rate of water flow in cubic meters per second ?
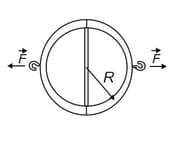
In , Otto von Guericke, the inventor of air pump, gave a demonstration before the noblemen of the Holy Roman Empire in which two teams of eight horses could not pull apart two evacuated brass hemispheres. (a) Assuming the hemispheres have (strong) thin walls, so that , in the figure, may be considered as both, the inside and the outside radius, show that the force required to pull apart the hemispheres has magnitude , where is the difference between the pressures outside and inside the sphere. (b) Taking as , the inside pressure as and the outside pressure as , find the force magnitude the teams of horses would have had to exert to pull apart the hemispheres. (c) Explain why one team of horses could have proved the point just as well, if the hemispheres were attached to a sturdy wall.