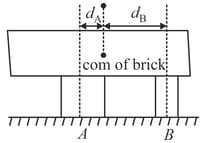
In the figure shown below, a lead brick rests horizontally on cylinders and . The areas of the top faces of the cylinders are related by , the Young's moduli of the cylinders are related by . The cylinders had identical lengths before the brick was placed on them. What fraction of the brick's mass is supported by cylinder and by cylinder ? The horizontal distances between the center of mass of the brick and the centerlines of the cylinders are for cylinder and for cylinder . What is the ratio ?

Important Questions on Equilibrium and Elasticity
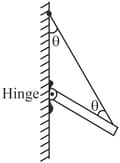
In the figure shown below, one end of a uniform beam of mass is hinged to a wall, the other end is supported by a wire that makes angles with both wall and beam. Find the tension in the wire and the magnitude and angle from the horizontal of the force of the hinge on the beam.
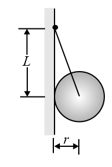
In the figure shown below, a cord with negligible mass suspends a uniform ball against a frictionless vertical wall. The ball's mass is , its radius is and the vertical distance between the ball's center and the cord attachment on the wall is the cord's tension and (b) the magnitude of the normal force on the wall from the ball? (Take )
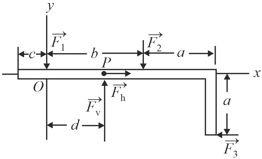
Forces and act on the structure, as shown in the figure in an overhead view. We wish to put the structure in equilibrium by applying a fourth force, at a point such as . The fourth force has vector components and . We are given that, and . Find , and .
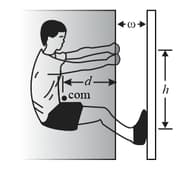
In the figure shown below, a climber is in a lie-back climb along a fissure, with hands pulling on one side of the fissure and feet pressed against the opposite side. The fissure has width and the center of mass of the climber is a horizontal distance from the fissure. The coefficient of static friction between the hands and the rock is and between the boots and the rock is (a) What is the least horizontal pull by the hands and push by the feet that will keep the climber stable? (b) For the horizontal pull of (a), what must be the vertical distance between the hands and the feet? If the climber encounters a wet rock, so that and are reduced, what happens to (c) the answer to (a) and (d) the answer to (b)?
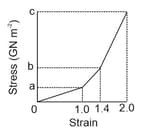
The figure below shows an approximate plot of stress versus strain for a spider-web thread, out to the point of breaking at a strain of . The vertical axis scale is set by values . Assume that the thread has an initial length of , an initial cross-sectional area of , and (during stretching) a constant volume. The strain on the thread is the ratio of the change in the thread's length to that of the initial length, and the stress on the thread is the ratio of the collision force to that of the initial cross-sectional area. Assume that the work done on the thread by the collision force is given by the area under the curve on the graph. Assume also that when the single thread snares a flying insect, the insect's kinetic energy is transferred to the stretching of the thread. (a) How much kinetic energy would put the thread on the verge of breaking? What is the kinetic energy of (b) a fruit fly of mass and speed and (c) a bumble bee of mass and speed ? Would (d) the fruit fly and (e) the bumble bee break the thread?