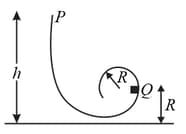
In the figure shown below, a single frictionless roller-coaster car of mass tops the first hill with speed at height
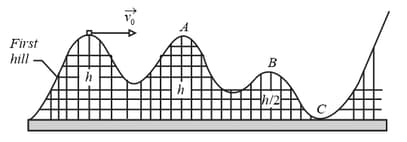
What is the speed of the car at (a) point , (b) point , and (c) point ? (d) How high will the car travel on the last hill, which is too high for it to cross? (e) If we substituted a second car with twice the mass. What then are the answers to parts (a) through (d)?


Important Questions on Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
You drop a book to a friend who stands on the ground at distance below. Your friend's outstretched hands are at a distance above the ground (In the figure shown below).
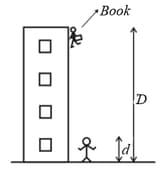
(a) What is the speed of the book when it reaches your friend's hands?
(b) If we substituted a second book with twice the mass, what would its speed be?
(c) If, instead, the book were thrown down, would the answer to part (a) increase, decrease, or remain the same?
In the figure shown below, a ice flake is released from the edge of a hemispherical bowl whose radius is The flake-bowl contact is frictionless.
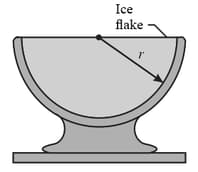
(a) What is the speed of the flake when it reaches the bottom of the bowl?
(b) If we substituted a second flake with twice the mass, what would its speed be?
(c) If, instead, we gave the flake an initial downward speed along the bowl, would the answer to part (a) increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A snowball is fired from a cliff high. The snowball's initial velocity is , directed above the horizontal.
(a)Using energy techniques, find the speed of the snowball as it reaches the ground below the cliff. What is that speed?
(b) if the launch angle is changed to below the horizontal and (c) if the mass is changed to ?
A marble is fired vertically upward using a spring gun. The spring must be compressed if the marble is to reach a target above the marble's position on the compressed spring.
(a) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the marble-Earth system during the ascent?
(b) What is the change in the elastic potential energy of the spring during its launch of the marble?
(c) What is the spring constant of the spring?
The figure shown below shows a ball with mass attached to the end of a thin rod with length and negligible mass. The other end of the rod is pivoted so that the ball can move in a vertical circle. The rod is held horizontally as shown and then given enough of a downward push to cause the ball to swing down and around and just reach the vertically up position, with zero speed there. How much work is done on the ball by the gravitational force from the initial point to,
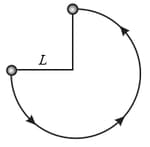
(a) What initial speed must be given to the ball so that it reaches the vertically upward position with zero speed? What then is its speed at (b) the lowest point and (c) the point on the right at which the ball is level with the initial point? (d) If the ball's mass were doubled, would the answers to (a) through (c) increase, decrease, or remain the same?
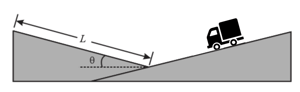
In the figure shown below, a runaway truck with failed brakes is moving downgrade at just before the driver steers the truck up a frictionless emergency escape ramp with an inclination of The truck's mass is (a) What minimum length must the ramp have, if the truck is to stop (momentarily) along with it? (Assume the truck is a particle and justify that assumption.) Does the minimum length increase, decrease, or remain the same if (b) the truck's mass is decreased and (c) its speed is decreased?
(c) What is the value of ? (d) If the block was released from a height above the spring, what would be the maximum compression of the spring?