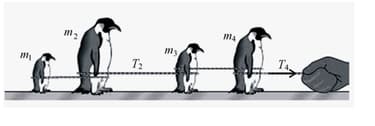
In the figure shown below shows four penguins that are being playfully pulled along very slippery (frictionless) ice by a curator. The masses of three penguins and the tension in two of the cords are , Find the penguin mass that is not given.


Important Questions on Force and Motion-I
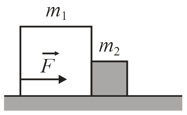
Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. A horizontal force is applied to the larger block, as shown in figure below.
(a) If and find the magnitude of the force between the two blocks.
(b) Show that if a force of the same magnitude is applied to the smaller block but in the opposite direction, the magnitude of the force between the blocks is which is not the same value calculated in (a).
(c) Explain the difference.
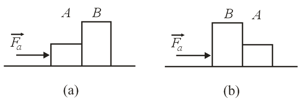
In the figure shown below , a constant horizontal force is applied to block , which pushes against block with a force directed horizontally to the right. In the figure shown below the same force is applied to block ; now block pushes on block with a force directed horizontally to the left. The blocks have a combined mass of . What are the magnitudes of their acceleration in the figure shown and force ?
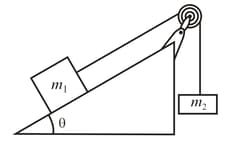
Two blocks of masses and are connected by a string as shown in Figure given below over a frictionless pulley of negligible mass. What is the acceleration magnitude of the two-block system if ?
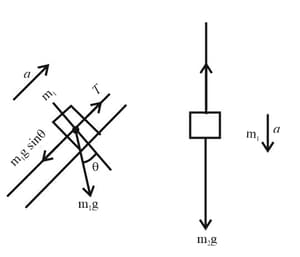
In the figure shown below a man sitting in a bosun's chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over a massless, frictionless pulley and back down to the man's hand. The combined mass of man and chair is. With what force magnitude must the man pull on the rope if he is to rise (a) with a constant velocity and (b) with an upward acceleration of ? (Hint: A free-body diagram can really help.) If the rope on the right extends to the ground and is pulled by a co-worker, with what force magnitude must the co-worker pull for the man to rise (c) with a constant velocity and (d) with an upward acceleration of? What is the magnitude of the force on the ceiling from the pulley system in (e) part a, (f ) part b, (g) part c, and (h) part d?
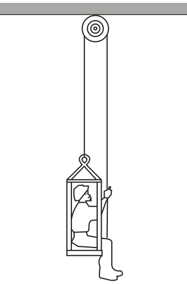
A Monkey climbs up a massless rope that runs over a frictionless tree limb and back down to a package on the ground in the figure shown below.
What is the magnitude of the least acceleration the monkey must have if it is to lift the package off the ground?
If, after the package has been lifted, the monkey stops its climb and holds on to the rope, what are the magnitude and direction of the monkey's acceleration and the tension in the rope?
In the figure shown below a block being pulled along a frictionless floor by a cord that applies a force of constant magnitude but with an angle that varies with time. When angle , at what rate is the acceleration of the block changing if
and
?
(Hint: The angle should be in .)
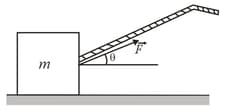
In the shot put, many athletes elect to launch the shot at an angle that is smaller than the theoretical one (about ) at which the distance of a projected ball at the same speed and height is greatest. One reason has to do with the speed the athlete can give the shot during the acceleration phase of the throw. Assume that a shot is accelerated along a straight path of length by a constant applied force of magnitude , starting with an initial speed of (due to the athlete’s preliminary motion). What is the shot's speed at the end of the acceleration phase if the angle between the path and the horizontal is and ? (Hint: Treat the motion as though it were along a ramp at the given angle.)
By what percentage is the launch speed decreased if the athlete increases the angle from to ?
