In the given arrangement, the space between a pair of co-axial cylindrical conductors is evacuated. The outer cylinder, called anode, may be given a positive potential relative to the inner cylinder.
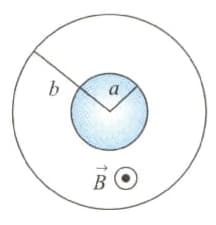
A static homogeneous magnetic field parallel to the cylinder axis, directed out of plane of figure is also present. Induced charges in the conductors are neglected.
We study the dynamics of electrons with rest mass and charge . The electrons are released at the surface of inner cylinder. Consider the following two cases :
Case 1 : Firstly the potential is turned on, but . An electron with negligible velocity is ejected at the surface of inner cylinder. It is found to hit the anode.
Case 2 : Now but is present. An electron starts out with an initial velocity in radial direction. For magnetic field larger than critical value the electron will not reach the anode.
The critical magnetic field is given by
Important Questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism
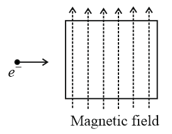
During its motion inside the chamber
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
| 1. Electron with | (i) | (P) |
| 2. Electron with | (ii) | (Q) |
| 3.Proton with | (iii) | (R) |
| 4. Proton with | (iv) | (S) |
In which case would the particle move in a straight line along the negative direction of y axis
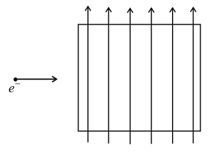
An electric field of appropriate magnitude is also applied so that the electron travels un-deviated without any change in its speed through the chamber. We are ignoring gravity. Then, the direction of the electric field is,
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
| 1. Electron with | (i) | (P) |
| 2. Electron with | (ii) | (Q) |
| 3.Proton with | (iii) | (R) |
| 4. Proton with | (iv) | (S) |
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
| 1. Electron with | (i) | (P) |
| 2. Electron with | (ii) | (Q) |
| 3.Proton with | (iii) | (R) |
| 4. Proton with | (iv) | (S) |
In which case will the particle describe a helical path with axis along positive z direction?
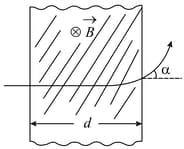
A rectangular region of dimensions has a constant magnetic field into the plane of the paper as shown. On one side the region is bounded by a screen. On the other side positive ions of mass and charge are accelerated from rest and towards the screen by a parallel plate capacitor at constant potential difference , and come out through a small hole in the upper plate. Which one of the following statements is correct regarding the charge on the ions that hit the screen?
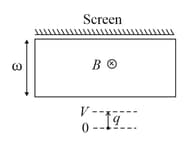
A proton (mass ) accelerated by a potential difference flies through a uniform transverse magnetic field . The field occupies a region of space by width . If be the angle of deviation of proton from the initial direction of motion (see figure), the value of will be: