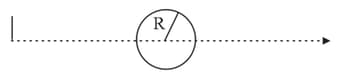
In the shown figure and are two concave mirrors of the same focal length . and are their principal axes, respectively. A point object is kept on the line at a distance from . The distance between the mirrors is . Considering two successive reflections first on and then on . The distance of the final image from the line is
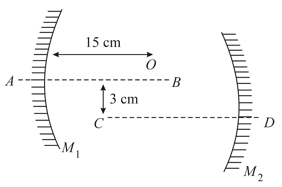


Important Questions on Ray Optics
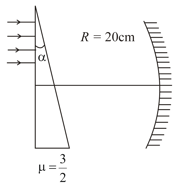
In the given figure a parallel beam of light is incident on the upper part of a prism of angle and R.I. . The light coming out of the prism falls on a concave mirror of radius of curvature . The distance of the point (where the rays are focused after reflection from the mirror) from the principal axis is
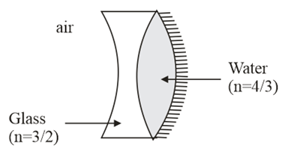
The figure showing the radius of curvature of the left and right surface of the concave lens are and , respectively. The radius of curvature of the mirror is , equivalent focal length of the combination is
STATEMENT-: A thin white parallel beam of light is incident on a plane glass-vacuum interface as shown. The beam may not undergo dispersion after suffering deviation at the interface (The beam is not incident normally on the interface.)
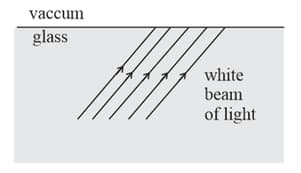
STATEMENT-: Vacuum has the same refractive index for all colours of white light.
In cases of real images formed by a thin convex lens, the linear magnification is
directly proportional to the image distance,
inversely proportional to the object distance,
directly proportional to the distance of image from the nearest principal focus,
inversely proportional to the distance of the object from the nearest principal focus.
From these, the correct statements are,
Rays from an object immersed in water traverse a spherical air bubble of radius . If the object is located far away from the bubble, its image as seen by the observer located on the other side of the bubble will be