List the applications of photoelectric effect.
Important Questions on Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
Explain the working of photo emissive cell. Write any two applications of photoelectric cells.
| 0.3 | 2.0 |
| 0.4 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.4 |
Given that Planck's constant (in units of ) found from such an experiment is :
Consider the following statements regarding the photoelectric effect experiment:
(I) Photoelectrons are emitted as soon as the metal is exposed to light.
(II) There is a minimum frequency below which no photo-current is observed.
(III) The stopping potential is proportional to the frequency of light.
(IV) The photo-current varies linearly with the intensity of the light.
Which of the above statements indicate that light consists of quanta (photons) with energy proportional to frequency?
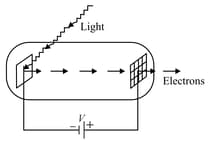
Light of wavelength falls on a cathode plate inside a vacuum tube as shown in the figure. The work function of the cathode surface is and the anode is a wire mesh of conducting material kept at a distance from the cathode. A potential difference is maintained between the electrodes. If the minimum de Broglie wavelength of the electrons passing through the anode is which of the following statement(s) is(are) true ?