EASY
Earn 100
List the different types of pulleys.
Important Questions on Simple Machine
MEDIUM
How is it possible to increase the M.A. of the given lever without increasing its length?
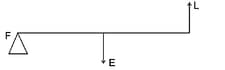
HARD
The diagram below shows a pulley arrangement:

Copy the diagram and mark the direction of tension on each stand of the string.
What is the velocity ratio of the arrangement?
If the tension acting on the string is, then what is the relationship between and effort ?
If the free end of the string moves through a distance , find the distance by which the load is raised.
EASY
The diagram below shows a claw hammer used to remove a nail:
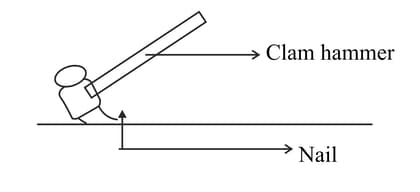
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) Give one more example of the same class of lever mentioned by you in (i) for which the mechanical advantage is greater than one.
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Forceps .
EASY
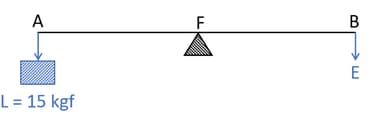
(a) To which class of lever does it belong?
(b) If , find its mechanical advantage,
(c) calculate the value of E.
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
A seesaw .


.png)