List the uses of recycled water.
Important Questions on Environmental Science
The greatest problem for water conservation is to reduce the amount of:
The Indus Valley civilization, that flourished along the banks of the River Indus and other parts of western and northern India about 5000 years ago, had one of the most sophisticated urban water supply and sewage systems in the world. The fact that the people were well acquainted with hygiene can be seen from the covered drains running beneath the streets of the ruins at both Mohenjo-daro and Harappa. Another very good example is the well-planned city of Dholavira, on Khadir Bet, a low plateau in the Rann in Gujarat. One of the oldest water harvesting systems is found about 130 km from Pune along Naneghat in the Western Ghats. A large number of tanks were cut in the rocks to provide drinking water to tradesmen who used to travel along this ancient trade route. Each fort in the area had its own water harvesting and storage system in the form of rock-cut cisterns, ponds, tanks and wells that are still in use today. A large number of forts like Raigad had tanks that supplied water.
In ancient times, houses in parts of western Rajasthan were built so that each had a rooftop water harvesting system. Rainwater from these rooftops was directed into underground tanks. This system can be seen even today in all the forts, palaces and houses of the region.
Underground baked earthen pipes and tunnels to maintain the flow of water and to transport it to distant places, are still functional at Burhanpur in Madhya Pradesh, Golkunda and Bijapur in Karnataka and Aurangabad in Maharashtra.
Where is one of the oldest rainwater harvesting system found?
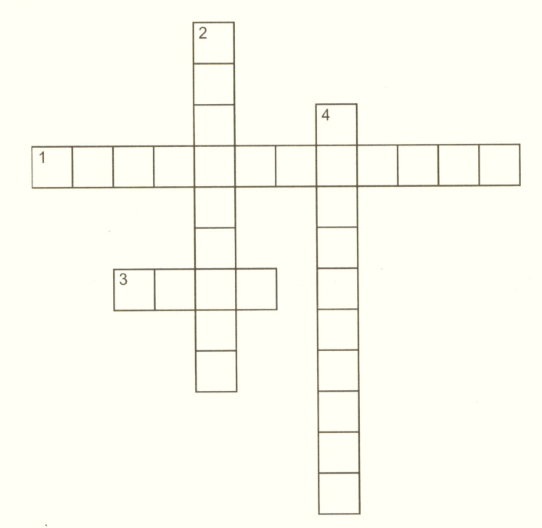
Across
1. The process of seeping of water into the ground
3. It is a type of irrigation
Down
2. The decrease in the water table due to overuse of groundwater
4. Rainwater______
What is meant by 'rainwater harvesting?
The Indus Valley civilization, that flourished along the banks of the River Indus and other parts of western and northern India about 5000 years ago, had one of the most sophisticated urban water supply and sewage systems in the world. The fact that the people were well acquainted with hygiene can be seen from the covered drains running beneath the streets of the ruins at both Mohenjo-daro and Harappa. Another very good example is the well-planned city of Dholavira, on Khadir Bet, a low plateau in the Rann in Gujarat. One of the oldest water harvesting systems is found about 130 km from Pune along Naneghat in the Western Ghats. A large number of tanks were cut in the rocks to provide drinking water to tradesmen who used to travel along this ancient trade route. Each fort in the area had its own water harvesting and storage system in the form of rock-cut cisterns, ponds, tanks and wells that are still in use today. A large number of forts like Raigad had tanks that supplied water.
In ancient times, houses in parts of western Rajasthan were built so that each had a rooftop water harvesting system. Rainwater from these rooftops was directed into underground tanks. This system can be seen even today in all the forts, palaces and houses of the region.
Underground baked earthen pipes and tunnels to maintain the flow of water and to transport it to distant places, are still functional at Burhanpur in Madhya Pradesh, Golkunda and Bijapur in Karnataka and Aurangabad in Maharashtra.
Do you think that rainwater harvesting can help in water conservation? Give reason to support your answer.

