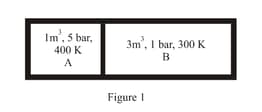
Mark the correct options.
A system is in thermal equilibrium with , but, not with . The system and may be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
A system is in thermal equilibrium with , but, not with . The system and are not in thermal equilibrium with each other.
A system is neither in thermal equilibrium with nor with . The system and must be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
A system is neither in thermal equilibrium with nor with . The systems and may be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
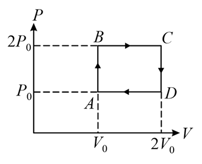
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:
[Heat of fusion of ice ; Specific heat of water ]
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
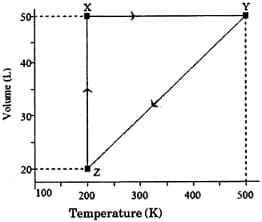
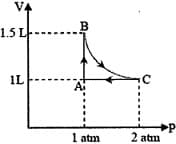
The pressure of the gas (in atm) at and respectively, are
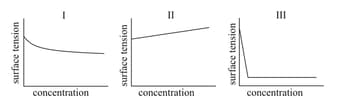
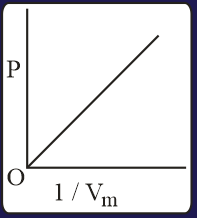
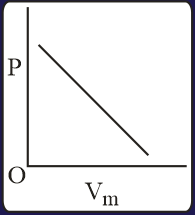
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
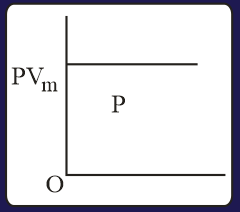
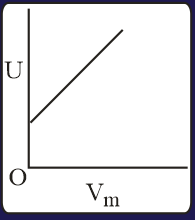
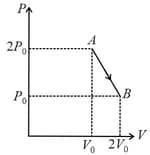
The three processes in a thermodynamic cycle shown in the figure are : Process is isothermal; Process is isochoric (volume remains constant); Process is adiabatic.
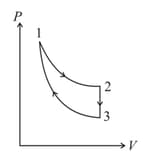
The total work done by the ideal gas in this cycle is, The internal energy decreases by, in the isochoric process. The work done by the gas in the adiabatic process is, . The heat added to the system in the isothermal process is
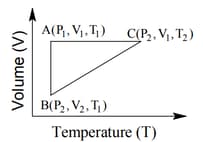
The correct option(s) is (are)
(Latent heat of ice is and )