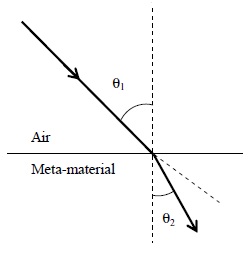
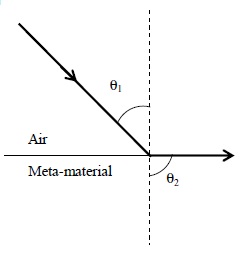
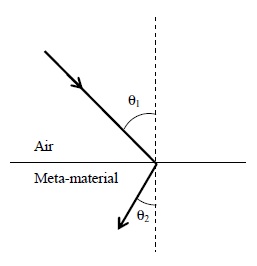
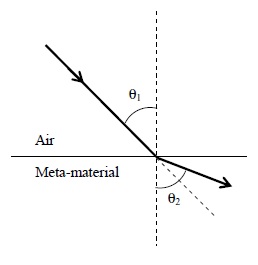
Most materials have the refractive index, n > 1. So, when a light ray from air enters a naturally occurring material, then by Snell's law, it is understood that the refracted ray bends towards the normal. But it never emerges on the same side of the normal as the incident ray. According to electromagnetism, the refractive index of the medium is given by the relation, where c is the speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum, v its speed in the medium, are the relative permittivity and permeability of the medium respectively.
In normal materials, both , are positive, implying positive n for the medium. When both are negative, one must choose the negative root of n. Such negative refractive index materials can now be artificially prepared and are called meta-materials. They exhibit significantly different optical behavior, without violating any physical laws.Since n is negative, it results in a change in the direction of propagation of the refracted light.However, similar to normal materials, the frequency of light remains unchanged upon refraction even in meta-materials.
For light incident from air on a meta-material, the appropriate ray diagram is
Important Questions on Light and Optical Instrument
Light enters from air to kerosene having refractive index of . What is the speed of light in kerosene, if the speed of light in air is ?
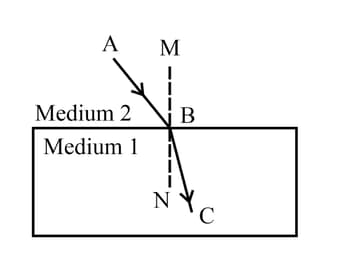
In the given figure, AB is the incident ray, BC is the refracted ray and MN is the normal at the point of incidence. Which medium is more
denser? Why?
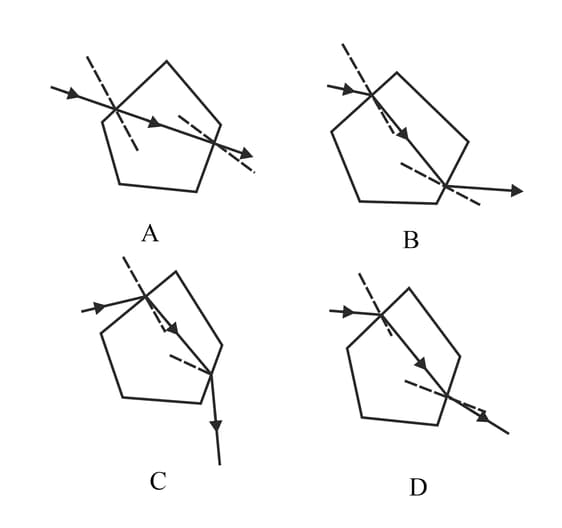
"Ray of light travels from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium, it moves towards normal and when it travels from optically denser to optically rarer medium it moves away from the normal is known as refraction of light". Which of the following pentagon figures shows the correct refraction of light.
Light enters from air to glass plate having refractive index. What is the speed of light in glass? (Given-speed of light in vacuum )
When a ray of light is incident perpendicularly on a transparent glass slab, what will be its angle of deviation?
What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air , and the refractive index of air with respect to water .
Between the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, which one is greater when light travels from a rarer to a denser medium?
If the refractive index of water with respect to air () is . Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water ().

