MEDIUM
Earn 100
Natural frequency is also known as eigenfrequency.
(a)True
(b)False
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Oscillations
HARD
EASY
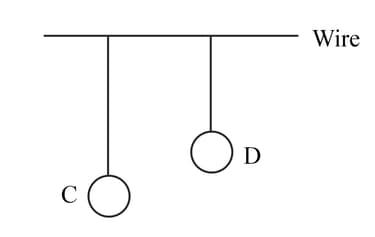
Two pendulums and are suspended from a wire as shown in the given figure. Pendulum is made to oscillate by displacing it from its mean position. It is seen that also starts oscillating. Name the type of oscillation, will execute.
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
A vibration tuning fork is placed over the mouth of a burette filled with water. The tap is opened and the water level gradually falls. It is observed that the sound becomes the loudest for a particular length of air column.
Why does the sound become the loudest?
HARD
If the amplitude of the particle is maximum for and the energy of the particle is maximum for then
EASY
MEDIUM
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
HARD
EASY
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
Describes the oscillatory motion of body in a dissipative medium under the influence of a periodic force, then the state of maximum amplitude of the oscillation is a phenomena of
MEDIUM

