On August , a large meteorite skipped across the atmosphere above the western United States and western Canada, much like a stone skipped across water. The accompanying fireball was so bright that it could be seen in the daytime sky and was brighter than the usual meteorite trail. The meteorite's mass was about ; its speed was about . Had it entered the atmosphere vertically, it would have hit Earth's surface with about the same speed. (a) Calculate the meteorite's loss of kinetic energy (in Joules) that would have been associated with the vertical impact. (b) Express the energy as a multiple of the explosive energy of megaton of , which is . (c) The energy associated with the atomic bomb explosion over Hiroshima was equivalent to kilotons of . To how many Hiroshima bombs would the meteorite impact have been equivalent?

Important Questions on Kinetic Energy and Work
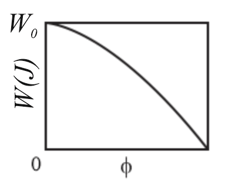
A force is applied to a bead as the bead is moved along a straight wire through displacement . The magnitude of is set at a certain value, but the angle between and the beads displacement can be chosen. Figure shown below gives the work done by on the bead for a range of values; . How much work is done by if is (a) and (b)?
(Given:- )
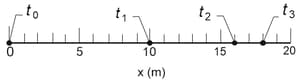
A bead with mass is moving along a wire in the positive direction of an -axis. Beginning at time when the bead passes through with speed a constant force acts on the bead. Figure shown below indicates the bead's position at these four times: , , and . The bead momentarily stops at . What is the kinetic energy of the bead at ?
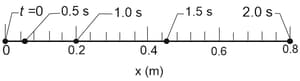
A body is at rest on a frictionless horizontal air track when a constant horizontal force acting in the positive direction of an -axis along the track is applied to the body. A stroboscopic graph of the position of the body as it slides to the right is shown in the figure shown below. The force is applied to the body at and the graph records the position of the body at intervals. How much work is done on the body by the applied force between and ?
A particle travels through a three-dimensional displacement given by If a force of magnitude
and with fixed orientation does work on the particle, find the angle between the force and the displacement if the change in the particle's kinetic energy is (a) and (b) .
