On the basis of kinetic theory of gases, the gas exerts pressure because its molecules:

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature obeys Maxwell's distribution.
Statement II : In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
An ideal gas in a closed container is slowly heated. As its temperature increases, which of the following statements are true ?
(A) the mean free path of the molecules decreases
(B) the mean collision time between the molecules decreases.
(C) the mean free path remains unchanged.
(D) the mean collision time remains unchanged.
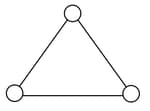
Consider a gas of triatomic molecules. The molecules are assumed to be triangular and made of massless rigid rods whose vertices are occupied by atoms. The internal energy of a mole of the gas at temperature T is:
Match the ratio for ideal gases with different type of molecules:
| Molecule Type | |
| (A) Monoatomic | (I) |
| (B) Diatomic rigid molecules | (II) |
| (C) Diatomic non-rigid molecules | (III) |
| (D) Triatomic rigid molecules | (IV) |
