HARD
Earn 100
One mole of an ideal gas (not necessarily monoatomic) is subjected to the following sequence of steps.
(a) It is heated at constant volume from
(b) It is expanded freely into a vacuum to double volume.
(c) It is cooled reversibly at constant pressure to .
Calculate and for the overall process.
Important Questions on Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
Match the following
| (A) | Isothermal process | (i) | |
| (B) | Adiabatic process | (ii) | |
| (C) | Isobaric process | (iii) | |
| (D) | Isochoric process | (iv) |
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
The magnitude of work done by a gas that undergoes a reversible expansion along the path shown in the figure is _________.
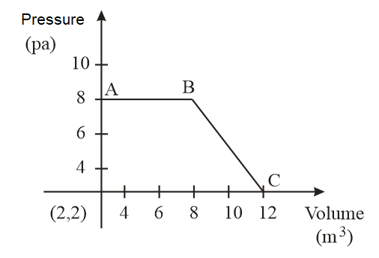
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
(Given,
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
Under the isothermal condition, a gas at expands from to against a constant external pressure of bar. The work done by the gas is
(Given that bar)
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.>Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other

