Only a few reactions are simple or straight forward, $i . e .$ purely first, second or third order reactions. But in most of the reactions, the interpretation of variety of data becomes difficult due to several other reactions taking place simultaneously along with the main reaction and thus smooth progress of the reaction is disturbed. Such reactions include the following different types. The reactions, in which a substance reacts or decomposes in more than one way, are called parallel or competing or side reaction. The reactions which take place exclusively on the walls of containing vessels are known as surface reactions. The reactions in which the products of chemical change react together to form the original reactants are called reversible reactions or opposing reactions or counter reactions. The reactions which proceeds from reactants to final products through one or more intermediate stages are called consecutive reactions.
The relation is valid for:
Important Questions on Chemical Kinetics
(Assume Activation energy and pre-exponential factor are independent of temperature; )
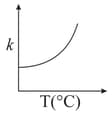
Consider the given plots for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation (and are rate constant and activation energy, respectively )
(I)
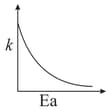
(II)
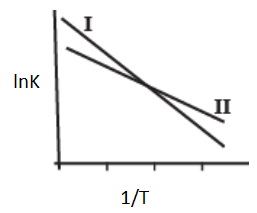
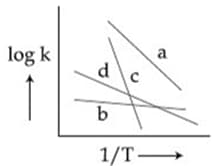
The Arrhenius plots of two reactions, I and II are shown graphically-
The graph suggests that-
It was found that the is decreased by in the presence of catalyst. If the rate remains unchanged, the activation energy for catalysed reaction is (Assume pre-exponential factor is same)
Identify the incorrect statement.
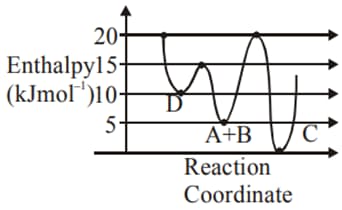
For a reaction, consider the plot of versus given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at is , then the rate constant at is:
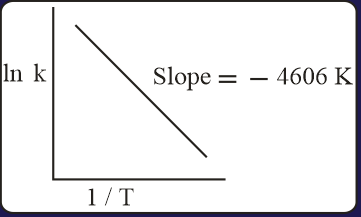
[Gas constant, ]

