Parallel rays, from the top of a distant object, incident on a concave mirror, form an image on the screen.
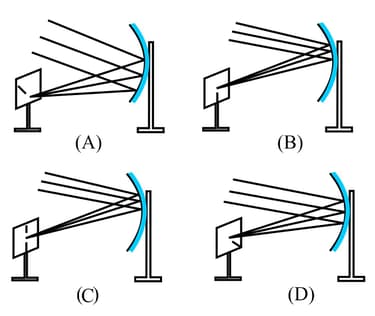
The diagram correctly showing the image of the object on the screen is-


Important Questions on Light - Reflection and Refraction
The focal length of the concave mirror in the experimental set-up, shown below, equals
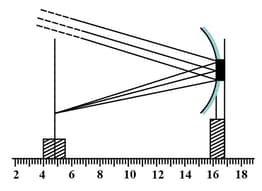
Image formed by a concave mirror-
To determine the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object we generally follow the following steps which are not in proper sequence
Hold the lens between the object and the screen.
Measure the distance between the lens and the screen.
Select a well lit distant object.
Place a screen opposite to the object on the lab table.
Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image.
The correct sequence of these steps is
To determine focal length of a concave mirror a student obtains the image of a well lit distant object on a screen. To determine the focal length of the given concave mirror he needs to measure the distance between—
Three students are finding the focal length of the given concave mirror by obtaining the image of the objects elected by them. obtains the image of the grill of the nearest window of the lab. obtains the image of a white painted building near the lab and obtains a point size image of the sun. The most correct value of the focal length is obtained by
Rajeev obtained the image of a distant object on a screen by using a concave mirror. To find the focal length of the mirror he should measure the distance between—
A student has to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. For getting best result he should focus—
A teacher gives a convex lens and a concave mirror of focal length of about each to his student and asks him to find their focal lengths by obtaining the image of a distant object. The student uses a distant tree as the object and obtains its sharp image, one by one, on a screen. The distance and between the mirror and the screen in the two cases and the nature of their respective sharp images are likely to be—
