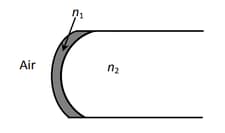
Parallel rays of light are falling on convex spherical surface of radius of curvature cm as shown. Refractive index of the medium is . After refraction from the spherical surface parallel rays
Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
For refraction at a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature from a medium of refractive index to medium of refractive index , establish the relation:
.
What will be behaver of a convex lens of the refractive index when it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index ?
[ Assume both surfaces of the lens have same radius of curvature ]
Where used symbols have their usual meanings
A light ray enters a solid glass sphere of refractive index at an angle of incidence . The ray is both reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle (in degrees) between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface is:
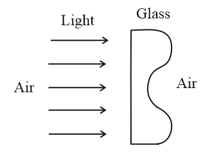
A parallel beam of light strikes a piece of transparent glass having cross section as shown in the figure below. Correct shape of the emergent wavefront will be (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)
A magician during a show makes a glass lens with disappear in a trough of liquid.
Could the liquid be water?
Derive an expression for refraction at a single(convex) spherical surface, i.e. a relation between (rarer medium) and (denser medium), where the terms have their usual meaning.
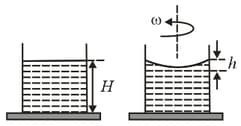
A beaker of radius is filled with water up to a height as shown in the figure on the left. The beaker is kept on a horizontal table rotating with angular speed . This makes the water surface curved so that the difference in the height of water level at the centre and at the circumference of the beaker is , as shown in the figure on the right. Take this surface to be approximately spherical with a radius of curvature Which of the following is/are correct? ( is the acceleration due to gravity)
A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index , as shown in the figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distance f2 from the film. Then