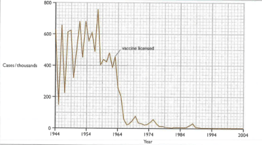
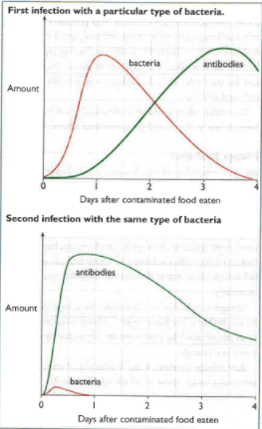
Predict and explain what would happen if the person is infected with a different kind of bacterium, after an immune response like the one in this figure.


Important Questions on Pathogens and Immunity
Copy and complete these sentences.
A microorganism that can make a person ill is called a__________. Some type of bacteria, _________, ___________ and ___________ are pathogens. Some pathogens can get into the body in food and drink. The stomach produces ____________, ___________ which helps to destroy these. The skin has a thick layer of _________ that stops most pathogens getting into it. However, if the skin is cut, pathogens may enter the blood. Blood _________ helps to prevent this. Many of the pathogens that are present in the air that we breathe in are prevented from reaching the lungs, because they are trapped by sticky __________ in the respiratory passages.
Active immunity, antibody, antigens, memory, cell, passive immunity, lymphocyte, phagocyte
- Resistance to infection by a particular pathogen, obtained by having the disease or being injected with a weakened pathogen
- Resistance to infection by a particular pathogen, obtained by acquiring antibodies from another organism
- Chemicals on the outer surface of a pathogen that is recognised as foreign by lymphocytes
- A type of white blood cell that ingests and digests bacteria
- A type of white blood cell that produces antibodies
- A long-lived cell produced by the division of activated lymphocytes
- A long-lasting type of immunity
- A protein produced by lymphocytes, which attaches to a specific antigen
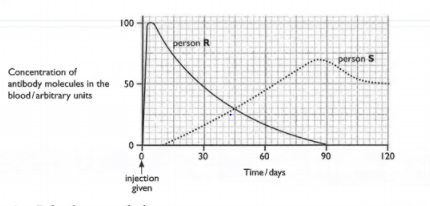
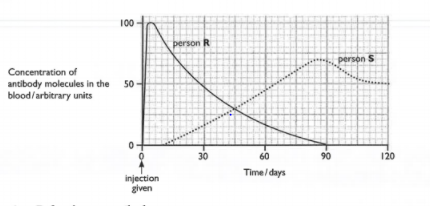
Explain why the concentration of antibody molecules shown in the graph decreased to zero in person R by day .
Explain why the concentration of antibody molecules shown in the graph for person S did not start to increase until days after the injection.
Describe the incidence of measles cases in the USA between and .