Read the passage carefully and answer the following questions.
The path of a light ray from air to two different media and for a given angle of incidence is as shown.
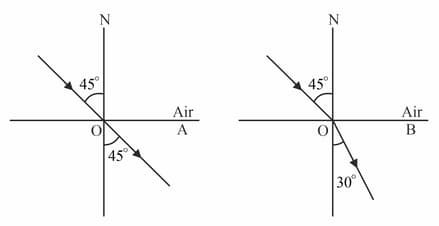
If angle of incidence is increased in both media, then angle of refraction will:
The path of a light ray from air to two different media and for a given angle of incidence is as shown.

Become zero in medium and will remain same in medium .

Important Questions on Light-Reflection and Refraction
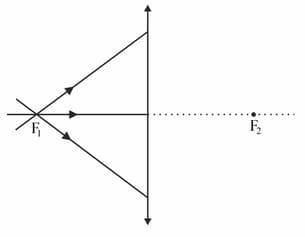
In the given diagram, three rays of light pass through focal point to the converging lens, placed along vertical line. Which of the following is correct regarding this?
A ray of light passing through a semicircular block (a denser medium) from air is shown below. Consider the given figure and select the correct option which correctly identifies the true (T) and false (F)?
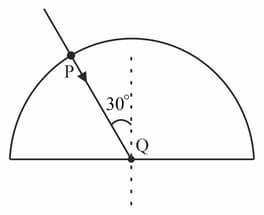
(i) There is no change in the direction of ray at because light ray incident on semicircular block at .
(ii) As light rays enters the semicircular block, its frequency remains the same.
(iii) Wavelength of light rays as it enters the block decreases.
(iv) Speed of light as it enters the block increases.
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | |
| (A) | ||||
| (B) | ||||
| (C) | ||||
| (D) |
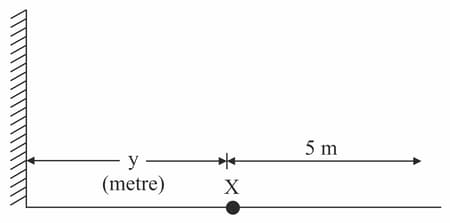
A man standing at a position in front of a plane mirror, at a distance of metre from the mirror as shown in figure. When the man moves away from the mirror, the new distance between the man and his image becomes metre. What is the value of ?
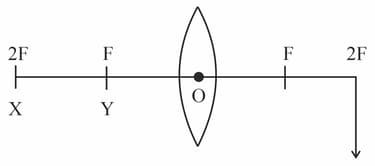
To produce an image by a convex lens, at the position shown (see figure) the object is needed to be placed:
When two plane mirrors are placed parallel and facing each other and an object is kept in between them, we get infinite images. But actually only a few images are visible because the intensity of the image is:
A rectangular block of glass has a refractive index . A pin is placed midway on the face . When observed from the face the pin shall:
Which of the following options is correct in case of a concave mirror?
| Object Position | Image Position | Size of image | Nature of Image | |
| (A) | At | At | Equal to object | Real and inverted |
| (B) | Beyond | Between and | Diminished | Virtual and erect |
| (C) | Between and | At infinity | Enlarged | Real and inverted |
| (D) | At | At infinity | Highly diminished | Virtual and erect |
